The advancement of technology has brought us to a point where digitalization is not only on our screens but also within our own bodies. What was once science fiction is becoming a reality with the so-called Internet of Bodies (IoB), a concept that extends the Internet of Things (IoT) to devices and sensors connected directly to the human body.
From smart pacemakers to experimental brain implants, IoB represents an unprecedented interconnection between biology and technology. These devices can monitor vital signs, administer personalized treatments, and even enhance physical and cognitive abilities. A clear example is implantable medical devices that transmit real-time information to doctors, allowing continuous monitoring of patients with chronic diseases.
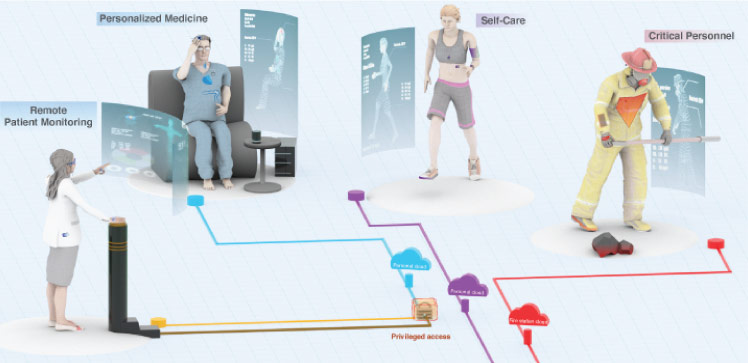
But IoB is not limited to healthcare. Wearable devices, such as smart rings and glasses, are already part of the personal digital ecosystem, collecting data on physical activity, sleep patterns, and even emotional states. With advances like electronic tattoos and ingestible biosensors, the line between biological and digital is becoming increasingly thin.
The impact of this technology also raises ethical and privacy concerns. Who controls the data generated by our own bodies? What happens if a company or government gains real-time access to our biometric information? Cybersecurity becomes a critical factor in this context, as the possibility of hacking implantable devices is a real threat that must be urgently addressed.
Despite these challenges, the potential of the Internet of Bodies is enormous. From improving quality of life to enabling new forms of interaction with the digital environment, this fusion between humans and technology is just beginning. In the coming years, we may see even bolder developments, such as advanced neural interfaces that allow direct communication between the mind and machines.
IoB is not just a technological evolution; it is a redefinition of what it means to be human in the digital age.





